Main advantages and disadvantages of BRep models
BRep modeling (Boundary Representation Modeling) is the most common type of modeling in CAD applications.
In short, a BRep is a mathematically precise representation of a 3D object that defines the geometric boundaries between solid and non-solid geometry.
The shape and contours of a BRep object are not constructed from reducible objects like polygons and vertices: BRep objects are defined by the mathematical relationships between surfaces.
Take a look at the bumper in the picture.
The bumper is not defined by small components like polygons, instead it exists as an independent object whose shape is defined by the position and curves of its surfaces relative to the XYZ axes in 3D space.
There are equations for the rotation of the surface, and the slight S-curve on the Y axis, and another for the elbow-like bump at the bottom of the bumper on the Z axis, and then you combine a zillion precise equations to describe every facet on every axis, and you have a BRep object.
| merit |
Disadvantages |
| BRep objects are mathematically accurate, enabling designers and engineers to build a “perfect” representation of their design. |
The BRep file format is heavy in nature and stores a lot of metadata that takes up disk space. |
| Unlike other modeling techniques, BRep allows you to "zoom in" without losing "resolution." BRep curves remain curves at any magnification. |
When visualization, rendering and animation are required, BRep just doesn't have the processing power. |
| The mathematical precision of BRep makes it ideal for manufacturing applications. |
Organic/natural objects are difficult to recreate with BRep's exact formulas |
Although BRep's characteristics make it an ideal format for manufacturing engineers and designers, it has significant limitations for visualization and rendering purposes.
The main advantages and disadvantages of polygon modeling

Polygonal (or polyhedral) modeling is the most common type of modeling in video game and animation studios.

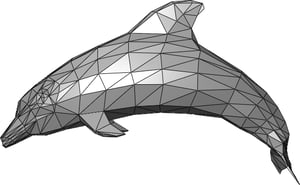
This type of modeling involves building 3D objects out of smaller components called "tris" (triangles) or "polys" (polygons).
A poly or tris is a perfectly flat shape, defined by the positions of its vertices (or points) and the edges that connect them.
Complex models of any shape can be built entirely from tries and polys. As designers demand higher fidelity designs (smoother surfaces, more detail, etc.), they can increase the polygon count of their models.
| merit |
Disadvantages |
| Polygonal models are the easiest to render and visualize, since modern computers are optimized to handle polygons. |
Modeling with polygons is imprecise and introduces human error. |
| Polygon modeling allows designers to create more unique and organic designs (humans, animals, etc.). |
Polygonal models are not compatible with all resolutions |
| Polygon models are created from smaller components (polys and tris) so they can deform and animate more naturally. |
Polygon modeling can be very time consuming, especially for complex designs. |
The characteristics of polygonal models make them suitable for applications where precision is not important and visual expression is important, which is why they are primarily used in animation studios and video game studios.
Main advantages and disadvantages of point cloud models
Point cloud modeling is typically used in the process of 3D scanning objects.
With point cloud modeling, rather than defining surfaces with mathematical formulas or creating surfaces from elementary shapes such as triangles, 3D objects are represented by a dense arrangement of vertices (points) along curved surfaces.
With sufficiently high resolution and point density, a point cloud model can accurately represent the features of almost any 3D object. In fact, point cloud 3D scanning is even used to create 3D representations of highly complex objects such as human faces.
Point cloud data has many applications beyond just scanning objects: it can also be used for simulations.
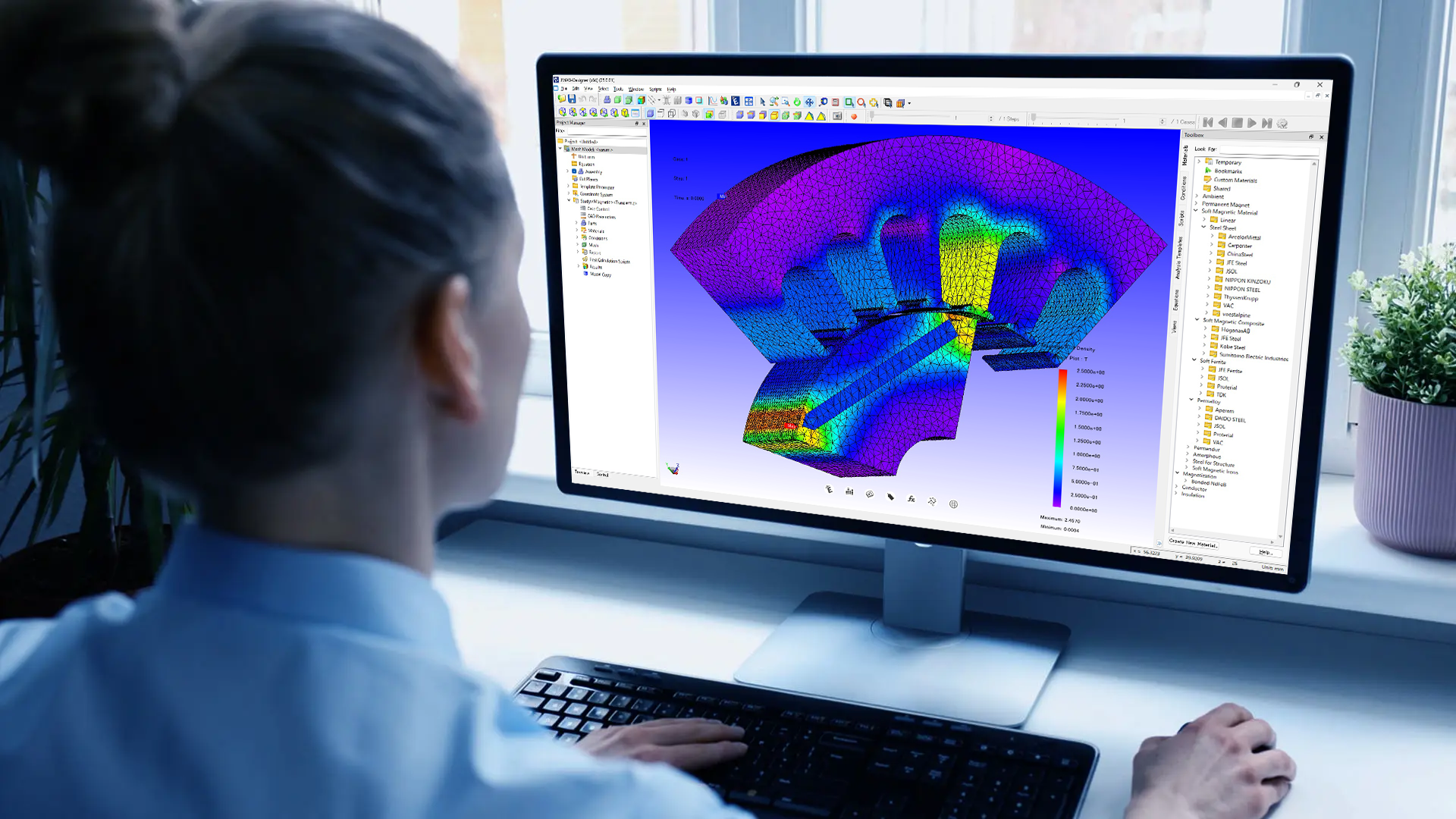
Point clouds can be used to represent solid objects in the context of finite element analysis, which reduces mathematically complex CAD surfaces to a relatively limited number of points, allowing engineers and scientists to do things like simulate objects under stress and how they deform.
| merit |
Disadvantages |
| Point cloud models can accurately represent relatively complex objects with a finite number of elements (points). |
Point cloud models are not as precise as BRep and cannot create mathematically perfect curves. |
| A point cloud model can be created most quickly using 3D scanning technology and CAD conversion software (creating one from scratch is not recommended). |
Point cloud data does not contain information about surfaces and therefore cannot be natively used for rendering or manufacturing. |
| |
Point cloud data is very difficult to convert into an accurate BRep or polygonal model. |
Ultimately, point cloud modeling alone isn't good for many applications. For a 3D scanned object to be truly useful, it needs to be converted into some other type of model. But when combined with other modeling types, point clouds can be very useful. Combined with BRep, you can simulate stress in your engineering models. And when used with polygon modeling, you can create complex 3D models of your scanned objects.
Main advantages and disadvantages of voxel modeling

A voxel in 3D is like a pixel in 2D.

First, let's consider what a pixel is: Everything you see on a computer screen is made up of very small squares called "pixels."
Most modern computers have "high resolution" displays that make them pixelated - they are so small and numerous that they are practically invisible, but instead letters, pictures, symbols, etc. appear smooth.
Voxels are essentially 3D pixels, but they are perfect cubes instead of squares.
In theory, voxels are the perfect modeling technique for replicating reality.
After all, our world is made up of things similar to voxels (but much smaller, and we call them "elementary particles"), and with high enough density (or "resolution") and the right rendering techniques, we can use voxels to recreate real-world objects that look and behave indistinguishably from the real thing.

But in reality, there is no mainstream way to easily create complex, high-resolution objects using voxels. There are some promising attempts, such as Atomontage, pictured above, but for really complex designs, the other modeling methods mentioned above are quicker and easier.
Furthermore, modern computers are not optimized for rendering voxels - most hardware is intended for rendering polygons, and high resolution voxel objects put a significant strain on current hardware.
Despite not being ready to go mainstream, voxel modeling currently has some very specific use cases:
Voxels are currently used in many scientific disciplines to rapidly determine volumetric data. For example, in voxel-based morphometry, researchers can use voxels to compare density differences in brain tissue. Geologists often use voxel modeling techniques to model geological features such as topography and elevation. In addition, voxel-based modeling can be used to visualize and measure the volume of everything from fluids to urban green spaces. Voxels are also useful for simulation techniques that require modeling of individual particles, such as simulating smart materials.
And that's where the true power of voxels comes into play.
The ability to represent complex objects in discrete, reducible units like particles makes it an extremely powerful tool for simulating the real-world behavior of complex objects.
| merit |
Disadvantages |
| Because voxels mimic particles, they are the most "precise" 3D building blocks of any other modeling type. |
It is very difficult to create complex objects using voxels without using expensive techniques like 3D scanning. |
| Voxels unlock new simulation methods not possible with other modeling techniques. |
Voxel modeling lacks the mathematical precision of BRep modeling. |
| Voxels are the easiest way to quickly model and visualize volumetric data, especially natural and organic formations. |
Current computer hardware is optimized for rendering polygons, and there is no specialized hardware available for efficiently rendering high-resolution voxels. |
The Hybrid Modeling Process
Hybrid modeling combines the benefits of the four major elements of 3D modeling: BRep, polygonal, point cloud, and voxel-based modeling, into one workflow.
Traditionally, you would need four different pieces of software to work with all of these model types: you would create the model in one method (such as BRep), then use a CAD conversion software to convert the BRep data to another format, where you could then open the file in another piece of software and make changes.
This is extremely tedious for a number of reasons.
What if you developed a new product using BRep and needed to quickly visualize or render it for promotional purposes? And what if your creative team recommended edits to the BRep after it was visualized?
What if you wanted to simulate a BRep model using point cloud data, and then apply the findings from that simulation back to the original BRep?
This requires going from one software to another, converting files and manually correcting them each time, which is not only time consuming but also prone to human error, which can be a huge cost in industries like CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) and CAE (Computer Aided Engineering).
This is where "hybrid modeling" comes in.
Software development kits like Spatial's CGM allow 3D developers to natively incorporate hybrid modeling capabilities into their toolset, allowing designers and engineers to seamlessly move between modeling types without losing data, and allowing engineers to run any simulation with BRep files and automatically adjust the results back into the model.
This movement between environments and modeling techniques is the process of hybrid modeling.
Powerful hybrid modeling software can speed up the model creation process and fill in typical gaps in 3D models (such as particle-based simulation of the behavior of engineering models).
Hybrid software recognizes these gaps and allows users to make adjustments along the way.
Hybrid Modeling as the Ultimate Solution
Good news for designers and engineers: it's no longer necessary to make a clear decision about which type of modeling is right for you.
Engineers, architects and designers across industries can now seamlessly transition between BRep, polygons, point clouds and voxels, leveraging the benefits of the different techniques and minimizing their drawbacks.
No one will ever say "you can't have the best of both worlds" again!
-1.webp)