Solid modeling technology in CAD environment
Solid modeling can start with any 2-3D design, such as a wireframe or sketch, or a basic geometric shape, such as a cube, sphere, cone, or cylinder.
You can then create a 3D model of any object you can imagine.
Easy right? …But it doesn't work that way.
The true complexity of solid modeling lies in its range of parametric capabilities and operators. Solid modeling allows the designer to manipulate and transform these basic solid shapes using a variety of operations such as "subtract" without losing the "solidity".
For example, "subtraction" is the process of modifying one (or more) features of a model, such as drilling a hole in an object, while preserving the original structure.
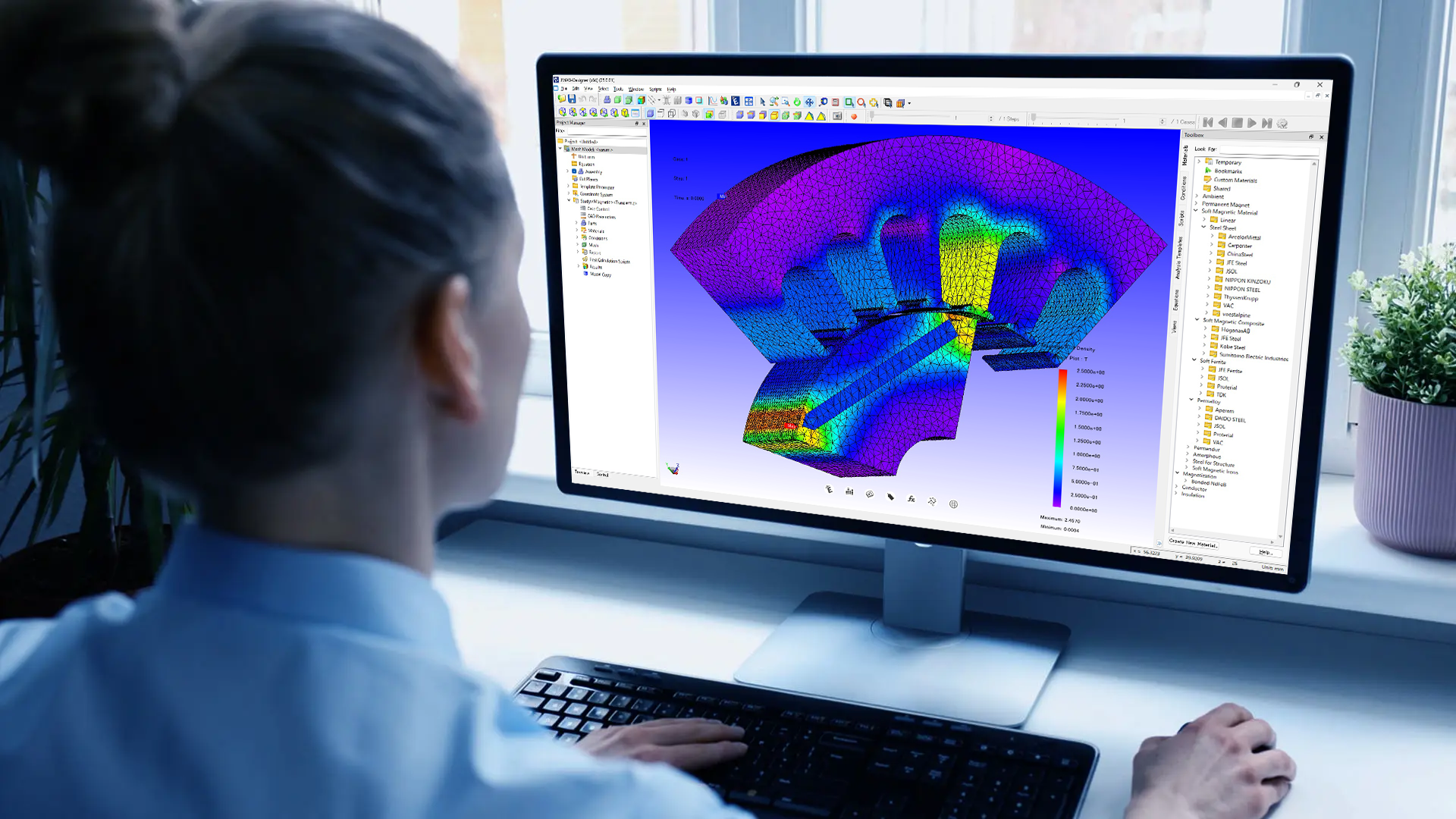
For this purpose, we use CAD software such as SolidWorks and AutoCAD, which are representative modeling systems.
But what exactly goes on in the background of this software?
Mathematical Foundations of Solid Modeling
When it comes to 3D design, solid modeling does all the heavy lifting. Solid modeling automatically calculates engineering equations that would be difficult to do by hand.
Solid modeling software must represent mechanical geometry with great accuracy, which is understandable given the intended use of the software.
When every aspect of a design is expressed as an equation, being able to easily solve complex mathematics is important, and that's solid modeling.
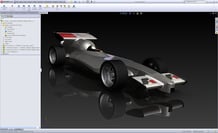
If an automaker wants to create a Formula 1 race car with perfect aerodynamic properties, they need to ensure that the dimensions laid out in the concept design are accurately reflected in their design software.
Imagine if supercars were manufactured with deviations of just a few millimeters at every angle.
Without this mathematical precision, it would be impossible to create (manufacture) a coherent object. Solid modeling and its computational power make this possible seamlessly.
Euclidean space
Every design component with a finite size and clear boundaries fundamentally needs a place where it can be expressed as a "tangible" design.
Euclidean space is a mathematically created environment in which parts can be added, removed, and modified.
Essentially, space is a theoretical background in which a set of points (or vertices) can be connected with their coordinates to create a 3D image.
This is actually the process of creating the initial wireframe design.
Important elements of solid objects
Solid modeling is further defined by four differentiators compared to wireframe and surface modeling :
- Complete - Classify various points of objects in the modeling environment as inside and outside (allowing for a more accurate representation of objects and their surfaces).
- Valid → Vertices, faces, and edges are properly connected for a complete view of the object
- No ambiguity → Every design aspect of the object has a single interpretation. (This means there is certainty and clarity in the design of the object, you know what it will actually look like.)
- Solids -> Consists of geometric and topological data (weight, shape, size, node/edge/face connectivity).
Real-world application
Solid modeling was originally created as a planning and validation tool for machining and assembly, but is now used in many other industries.
3D modeling software isn't just for engineers anymore.
It is used not only in product design, but also in interior design, 3D printing, and other media such as games and movies.
As the proliferation of open source modeling software shows, the future of solid modeling and 3D software has only just begun.
-1.webp)